Helicobacter Pylori (H. pylori), Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
It is a known fact that H. pylori bacteria are present in 50% to 75% of the world’s population, mostly in children, and although it could not cause any symptoms, yet H. pylori testing Dubai is more than essential for effective treatment.
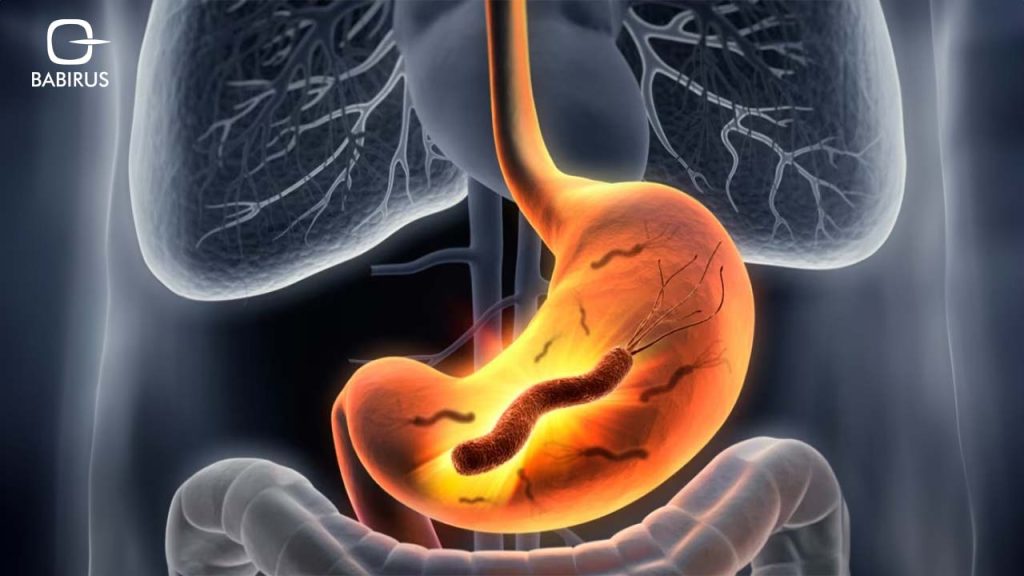
Moreover, the H. pylori bacterium infects the stomach lining and could lead to various gastrointestinal issues such as gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even gastric cancer.
In this article, we will discuss all about the H. pylori testing Dubai, with the H. pylori symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and H. pylori treatment.
What Are Helicobacter Pylori (H. pylori)?
Helicobacter pylori, commonly referred to as H. pylori, is a bacterium that primarily resides in the human stomach. That was first discovered in 1982 by Australian scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2005 for their groundbreaking work on this microorganism.
H. pylori testing Dubai helps define the infection, which could mainly occur through person-to-person contact, often from family members or close contacts. Moreover, a person could be infected through contaminated food, water, or utensils, as well as via oral-fecal transmission.
Popular H. Pylori Symptoms:
The symptoms of H. pylori infection can vary from person to person, but some common indicators include:
Abdominal Pain:
One of the most common symptoms of H. pylori infection is abdominal pain, which can be either constant or intermittent and may be localized to the upper-right quadrant of the abdomen, where the stomach is located.
The pain can be worse after eating, at night, or when lying down.
Dyspepsia:
Dyspepsia, also known as indigestion, is a general term for discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen.
Helicobacter pylori infection can cause dyspepsia, which may present as a burning sensation, fullness, or bloating after eating.
Nausea and Vomiting:
H. pylori infection can lead to nausea and vomiting, particularly in cases of severe inflammation or ulcers.
Keep in mind, that these symptoms may be more noticeable when the stomach is empty or after eating certain trigger foods.
Blood in Stools:
The blood in the stool could be due to the fact that Helicobacter pylori infection could cause bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
This can appear as bright red blood or dark, tarry stools, however, this symptom could be a sign of a more serious complication, such as an ulcer or gastritis.
Weight Loss:
Unexplained weight loss can be a sign of an underlying health condition, such as Helicobacter pylori infection.
This may be due to a decrease in appetite, malabsorption of nutrients, or the presence of an ulcer that causes discomfort during meals.
Anemia:
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not produce enough red blood cells and the H. pylori infection could cause it.
Leading to other symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
The Main 5 H. Pylori Causes:
The key causes of H. pylori infection are multifactorial, involving a combination of factors that contribute to the transmission and prevalence of the bacterium:
1. Ingestion of Contaminated Food and Water:
Consuming food and water that have been contaminated with the H. pylori bacteria is one of the most common infection reasons.
The fecal-oral infection occurs when the bacteria enter the body when someone eats contaminated water or food with feces.
Moreover, in areas where public health and hygiene are poor, there is a much higher risk of developing H. pylori infection.
2. Person-to-Person Transmission:
H. pylori can also be spread from one person to another, often through close contact with an infected individual, often through sharing of utensils, and toothbrushes, or direct contact with saliva.
Household members, mostly children, are at an increased risk of getting the infection due to close living quarters and frequent contact.
3. Poor Hygiene and Sanitation Practices:
People who do not wash their hands often, especially after going to the bathroom, changing a baby’s diapers, or touching raw meat, can spread the bacteria.
As the poor hygiene and lack of cleanliness, especially in the kitchen, can also make it easier for the bacteria to spread.
4. Living in Developing Countries:
Individuals living in developing countries are at a higher risk of contracting H. pylori infection due to factors such as poor sanitation, limited access to clean water, and overcrowded living conditions.
Additionally, these factors contribute to the increased occurrence of the bacterium in these regions.
5. Genetic Factors:
Some studies have suggested that genetic factors may play a role in the exposure to H. pylori infection, as some genetic variations may make an individual more vulnerable to the bacterium, while others may provide some level of autoimmunity.
Effective H. Pylori Diagnosis Methods:
Diagnosing H. pylori infection is vital to achieve the best management and treatment. There are several methods available for diagnosing H. pylori, which can be categorized into invasive and non-invasive techniques:
Invasive Methods:
Non-Invasive Methods:
The H. Pylori Testing Dubai:
Early detection and treatment of this bacteria are vital to maintain good health. Furthermore, in Dubai, various diagnostic centers and hospitals offer H. pylori testing services to help individuals determine if they are infected with the bacteria, including:
Current H. Pylori Treatment:
The standard treatment for H. pylori infections usually consists of:
This combination is designed to target and eliminate the H. pylori bacteria, while the PPI helps to reduce stomach acid production, which can help to ease symptoms and empower the antibiotics’ effect and work.
Usually, H. pylori infections require a two-week course of treatment, however, some people might need a longer course of treatment or perhaps a different combination of antibiotics. Thus, it is better to consult a professional healthcare practitioner to set the best course of action in such circumstances.
On the other hand, patients should modify their food and lifestyle in addition to receiving antibiotics in order to lower their chance of H. pylori reinfection and improve their overall gut health.
These adjustments could include:
Last but not least,
H. pylori infection can cause various symptoms, and early detection and treatment are vital to prevent serious complications. Thus, understanding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options will help individuals take appropriate steps to manage and treat this bacterial infection.
Take care of your health with Babirus Medical Equipment, and contact us to benefit from the updated molecular diagnostics test for the early detection of H. pylori.